Appendicectomies
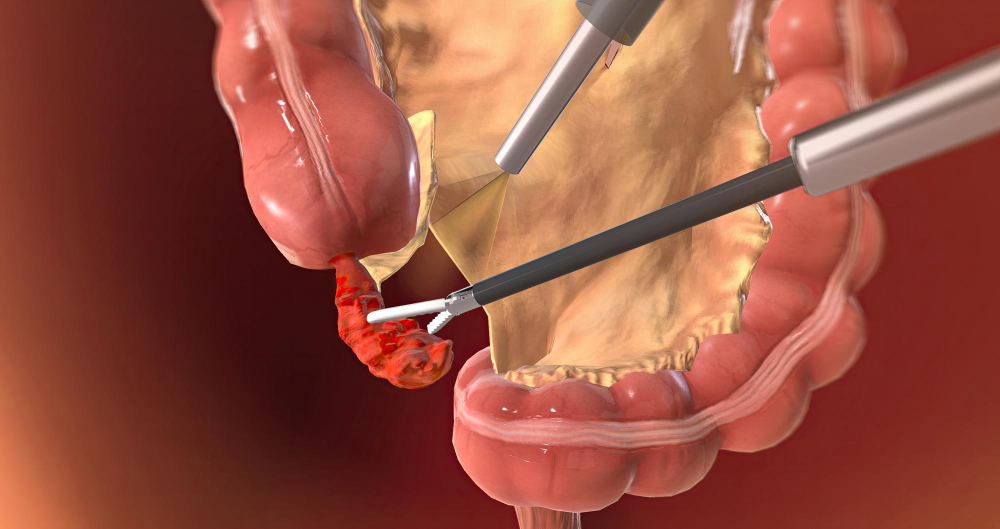
Appendicectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove the appendix, typically due to inflammation or infection, known as appendicitis. Traditionally, appendicectomies were performed using open surgery, which involves making a larger incision in the abdomen. However, in recent years, minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopic and robotic-assisted surgery, have become increasingly popular for performing appendicectomies.
Laparoscopic appendicectomy involves making several small incisions in the abdomen through which specialized surgical instruments and a tiny camera called a laparoscope are inserted. The laparoscope provides a magnified view of the abdominal organs on a monitor, allowing the surgeon to visualize the appendix and surrounding tissues more clearly. The appendix is then carefully dissected and removed through one of the small incisions. Laparoscopic appendicectomy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and improved cosmetic outcomes.
Robotic-assisted appendicectomy is a variation of laparoscopic surgery that utilizes robotic technology to assist the surgeon in performing the procedure. The surgeon controls robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments from a console, allowing for greater precision and dexterity during the operation. The robotic system provides enhanced visualization and maneuverability, making it particularly useful for complex cases or in patients with anatomical variations. Robotic-assisted appendicectomy offers similar benefits to laparoscopic surgery, including less pain, quicker recovery, and smaller scars.
Both laparoscopic and robotic-assisted appendicectomies are generally considered safe and effective procedures with low complication rates. However, they may not be suitable for all patients, particularly those with severe inflammation, perforation, or other complications of appendicitis. In such cases, open surgery may be necessary to ensure complete removal of the appendix and proper management of any associated complications.
Overall, minimally invasive appendicectomy techniques have revolutionized the treatment of appendicitis by offering patients a less invasive alternative to traditional open surgery. These techniques have significantly improved patient outcomes, resulting in shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and reduced postoperative pain. However, the choice of surgical approach should be based on individual patient factors, surgeon expertise, and the specific characteristics of the case.