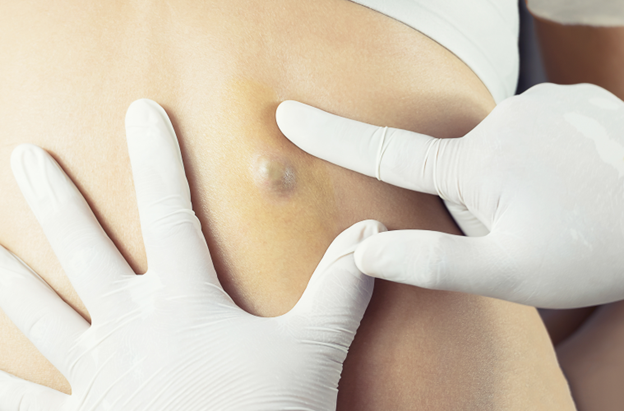
What is a Sebaceous Cyst?
Sebaceous cysts are small, round, and usually firm lumps beneath the skin. They develop when sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing sebum (an oily substance that lubricates the skin and hair), become blocked. This blockage causes sebum to accumulate within the gland, forming a cyst. The cyst often feels smooth to the touch and can vary in size from very small to several centimeters across.
Although sebaceous cysts are typically harmless, they can cause discomfort if they become infected, inflamed, or large enough to press against other structures under the skin.
Causes of Sebaceous Cysts
Several factors can contribute to the formation of sebaceous cysts. Some of the most common causes include:
- Blocked Hair Follicles: The most common cause of sebaceous cysts is the blockage of hair follicles. When a follicle becomes clogged with excess sebum, dead skin cells, and keratin, a cyst can form.
- Trauma to the Skin: Physical injury or irritation to the skin, such as a cut or surgical wound, can sometimes lead to the formation of a sebaceous cyst. The injury can cause the skin to repair in a way that traps sebum inside, leading to a cyst.
- Genetics: In some cases, sebaceous cysts may run in families. If a close relative has had cysts, there may be an increased risk of developing them.
- Acne: People with acne-prone skin are at a higher risk of developing sebaceous cysts due to the excessive production of sebum and frequent blockages of hair follicles.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially during puberty, pregnancy, or menstruation, can lead to increased sebum production, increasing the risk of cyst formation.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Some underlying medical conditions, such as Gardner’s syndrome or basal cell nevus syndrome, can cause multiple sebaceous cysts to develop.
Symptoms of Sebaceous Cysts
Sebaceous cysts typically present as a small, round lump beneath the skin. The most common symptoms of sebaceous cysts include:
- A Firm, Smooth Lump: The cyst feels firm to the touch and may move slightly when pressed. It can be located anywhere on the body but is most commonly found on the face, neck, back, and scalp.
- A Small Pore or Opening: Some sebaceous cysts have a small, dark opening at the center. This opening, called a punctum, is where the sebum or other materials may occasionally drain out.
- Size Variation: Sebaceous cysts can range in size from very small to several inches across. The size of the cyst may fluctuate over time as it fills with more material or if it becomes infected.
- Pain or Tenderness: Sebaceous cysts are typically painless unless they become infected or inflamed. If an infection occurs, the area around the cyst may become red, swollen, and tender to the touch.
- Possible Drainage: In some cases, the cyst may rupture or leak a thick, yellowish substance. This is typically the sebum, keratin, and other materials that accumulated inside the cyst. If this happens, the cyst may shrink in size, but it is important to seek medical attention to prevent further infection.
Diagnosis of Sebaceous Cysts
In most cases, sebaceous cysts are diagnosed through a physical examination. A healthcare provider will examine the lump and inquire about your symptoms, medical history, and any recent trauma to the skin.
In some instances, if the cyst appears unusual or if there are concerns about an underlying condition, further diagnostic tests may be recommended. This could include:
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create an image of the cyst and assess its size and structure.
- Biopsy: In rare cases, a biopsy may be necessary to rule out other types of growths or to confirm that the cyst is benign.
Treatment Options for Sebaceous Cysts
Most sebaceous cysts do not require medical treatment unless they cause discomfort, pain, or cosmetic concerns. Treatment options include:
- Observation: If the cyst is small, painless, and not causing any problems, your doctor may recommend simply monitoring it over time. Many sebaceous cysts will remain stable or even disappear on their own without the need for intervention.
- Drainage: If the cyst becomes infected or painful, your doctor may choose to drain the cyst to relieve pressure and discomfort. This procedure involves making a small incision in the cyst and allowing the contents to drain out. However, drainage alone may not prevent the cyst from returning.
- Surgical Removal: For persistent, large, or bothersome cysts, surgical removal may be the most effective option. In this procedure, the entire cyst (including its capsule) is carefully removed from the skin. This ensures that the cyst is less likely to return. Surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia, and recovery time is usually minimal.
- Antibiotics: If a sebaceous cyst becomes infected, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection and reduce inflammation. However, antibiotics alone will not remove the cyst, and surgery may still be necessary.
- Steroid Injections: In some cases, a doctor may recommend steroid injections to reduce inflammation and help shrink the cyst.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While sebaceous cysts are generally harmless, you should consult a healthcare provider if:
- The cyst becomes painful, red, or swollen, which could indicate infection.
- The cyst continues to grow despite attempts at draining or treatment.
- The cyst ruptures or drains a foul-smelling substance.
- You notice any unusual changes in the appearance of the cyst.
Prevention of Sebaceous Cysts
There is no guaranteed way to prevent sebaceous cysts, but some steps may help reduce the risk of developing them:
- Practice good skin hygiene by regularly cleaning your skin with mild soap and water.
- Avoid squeezing or popping cysts, as this can increase the risk of infection.
- If you are prone to acne, seek appropriate treatment to manage your skin condition.
- Protect your skin from trauma or injury, which can lead to cyst formation.
Conclusion
Sebaceous cysts are common and typically harmless growths that form beneath the skin. While they are usually not a cause for concern, they can cause discomfort or cosmetic issues. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sebaceous cysts can help you manage them effectively. If you are experiencing symptoms or have concerns about a sebaceous cyst, it is important to consult a healthcare provider to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment